Cain and Abel is a password recovery tool that is often used in the field of cybersecurity. It is primarily designed for Microsoft Windows operating systems and has functionalities related to network analysis and password cracking. Here are some key aspects of Cain and Abel:
- Password Cracking: Cain and Abel can be used to perform various types of password attacks, including dictionary attacks, brute-force attacks, and cryptanalysis attacks. It aims to recover passwords stored on a system.
- Sniffing and Spoofing: The tool has the capability to perform network sniffing and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. It can capture and analyze network traffic, making it useful for understanding and exploiting vulnerabilities in network security.
- Cryptanalysis: Cain and Abel can conduct cryptanalysis attacks on hashed passwords. It supports various cryptographic algorithms and techniques for breaking password hashes.
- ARP Spoofing: The tool can perform ARP spoofing, a type of attack where the attacker sends false Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages on a local area network. This can lead to various security issues, including man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Certificate Spoofing: Cain and Abel can also be used for certificate spoofing, allowing attackers to create fake SSL certificates to intercept secure communications.
- Wireless Network Attacks: The tool includes features for attacking and cracking wireless network protocols, such as WEP and WPA/WPA2. This makes it a potential tool for unauthorized access to Wi-Fi networks.
It’s important to note that while Cain and Abel has legitimate use cases for security professionals and system administrators, its misuse for unauthorized purposes, such as hacking or cracking passwords without proper authorization, is illegal and unethical. Responsible and ethical use of such tools is crucial to maintaining the integrity and security of computer systems and networks.
Let’s see Cain & Abel in action:
Below are some use cases of Cain & Abel, shown ip/host info are for informational purpose.
How to perform Host Discovery using Cain & Abel:
Start Cain & Abel from the desktop.

Navigate to the Sniffer tab.

Now, from the Sniffer tab and Hosts sub-tab, run a MAC Address scan by clicking on the highlighted button.

Click on OK to continue with the MAC address scan.

Soon, the hosts will appear in the table.
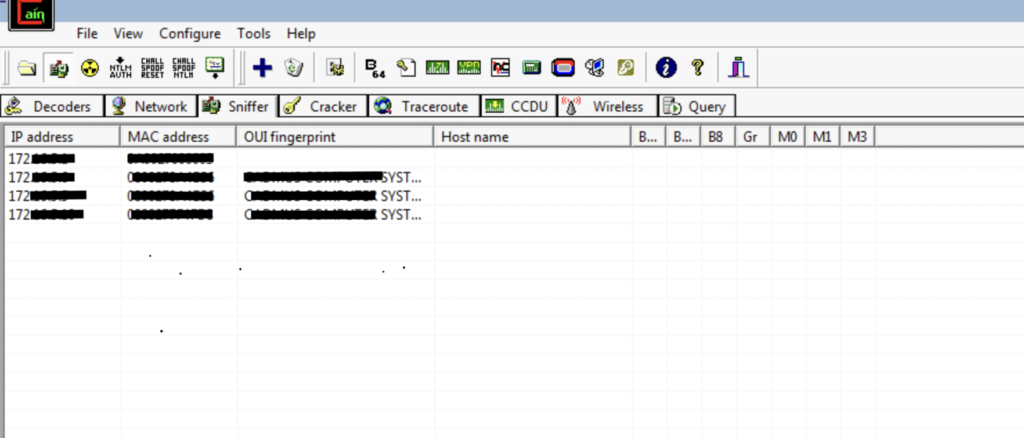
What is the protocol used by the Cain & Abel to perform host discovery?
The answer is ARP. You can prove that by running Wireshark and sniffing the traffic on Local Area Network 2.
Using the previous technique, can you list the online hosts from another network i.e.: *10.x.x.0/24*? If it didn’t work, can you explain why?
We cannot perform host discovery from a different network using the ARP protocol. Host discovery with ARP just works when all hosts are on the same broadcast domain.
The Scan Mac Address feature works by sending ARP requests to the broadcast address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff asking for specific IP address range (if specified). ARP is a protocol used for the resolution of network layer addresses (IP address) into link-layer addresses (MAC address). It works on the layer 2 of the OSI model, so it can only be used to discovery hosts which are located in the same subnet.
As you can see from the previous screenshot, many ARP packets were sent in broadcast. However, ARP replies were only obtained from the hosts which are alive, e.g.: 172.x.x.x
ARP Poisoning
From the audit host (172.x.x.x), launch an ARP Poisoning Attack using Cain & Abel against all identified hosts.
From the Sniffer component, select the ARP tab.
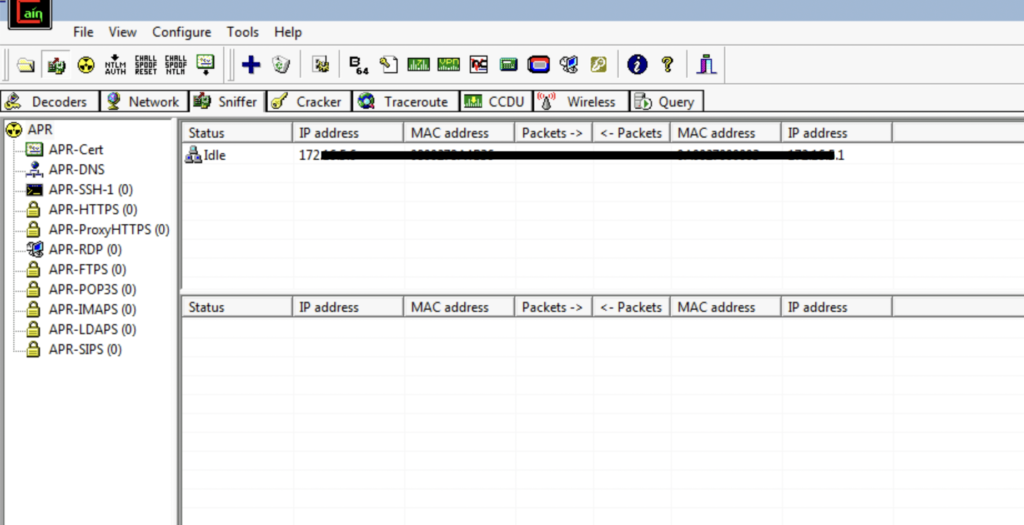
To configure a new ARP Poisoning routing, give focus on the first table and click the “plus” button from the toolbar.


Since we have to hijack the traffic between 172.x.x.x ,172.x.x.x and 172.x.x.x and its gateway, Select the target on the left table, select the gateway machine on the right table and click “OK”.

The table will be populated with the first target mapping.
Repeat the process for the rest of the targets. And start the ARP poisoning attack by clicking the “hazard” Start/Stop ARP button.
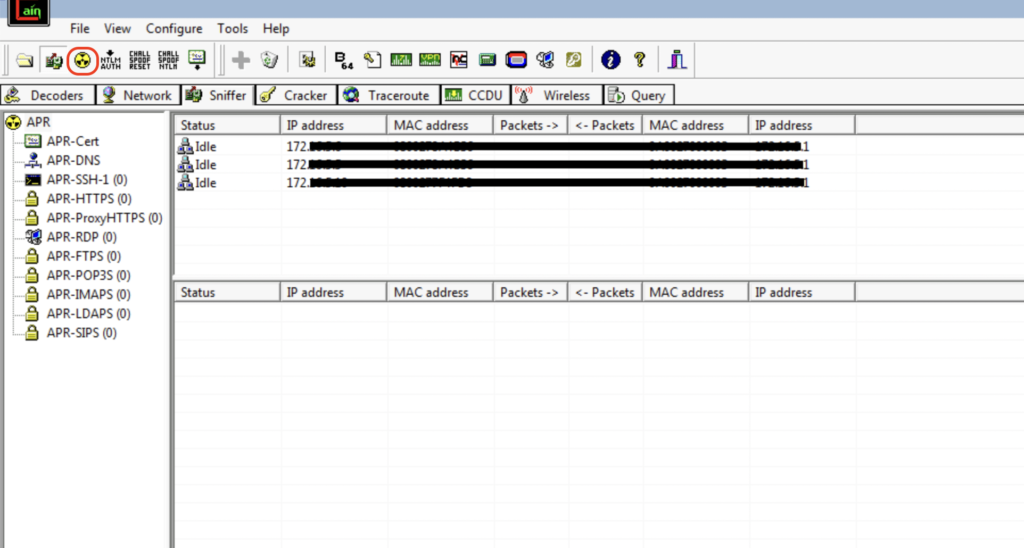
Once the attack is on, the status should change from Idle to Poisoning.

Inspect the passwords.
Stop the ARP Poisoning Attack launched from the host 172.x.x.10 and identify the FTP credentials.
Stop the ARP Poisoning Attack by clicking the Sniffer and ARP buttons from the toolbar menu. Navigate to the Passwords tab.

On the left menu, we can notice the FTP and SMB protocol tabs are highlighted.
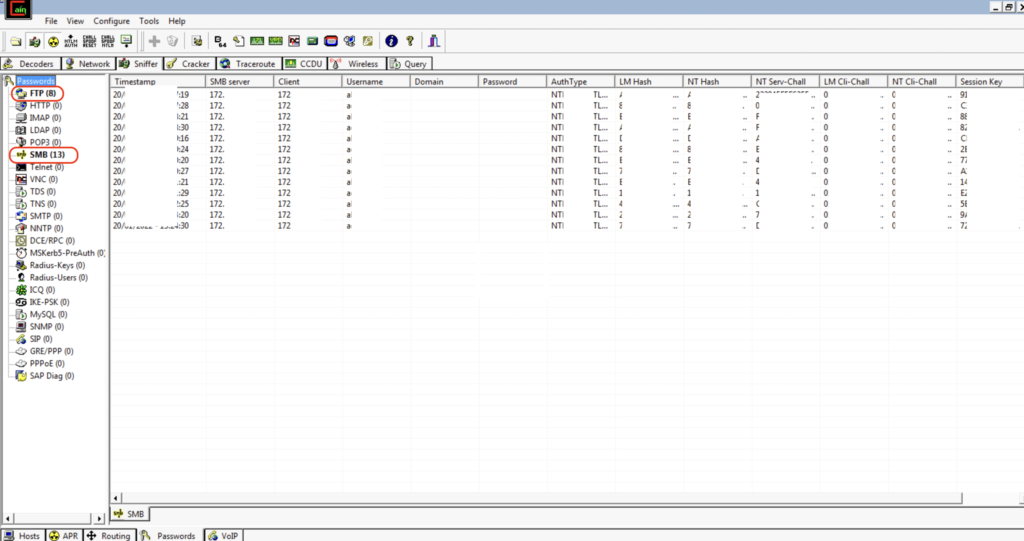
Click on the FTP tab.
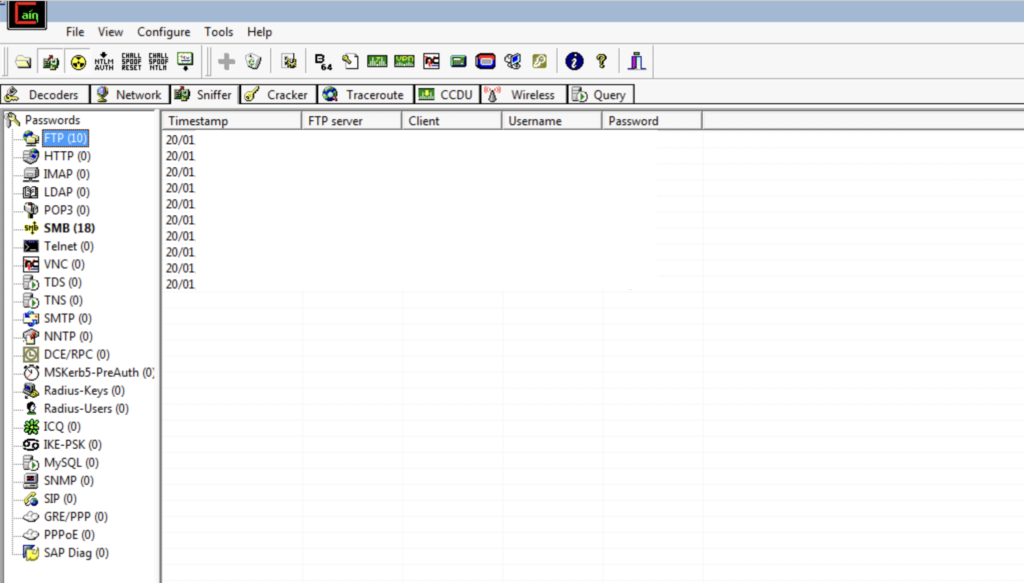
FTP Credentials
The captured FTP Credentials can be seen by selecting the Password tab within the Sniffer Component and then selecting FTP from the menu:
| FTP Server IP Address | 10.x.x.6 |
|---|---|
| Username | admin |
| Password | pa$$ |
ARP Poisoning Analysis
Analyze the results of the ARP Poisoning attack and check if there is any SMB connection. Then, crack the password, it will be useful later.
Apart from FTP credentials, the attack was able to capture SMB data as well. Navigate to the SMB tab.

Select a row, right-click on it, and click on Send to Cracker

Navigate to the cracker tab:
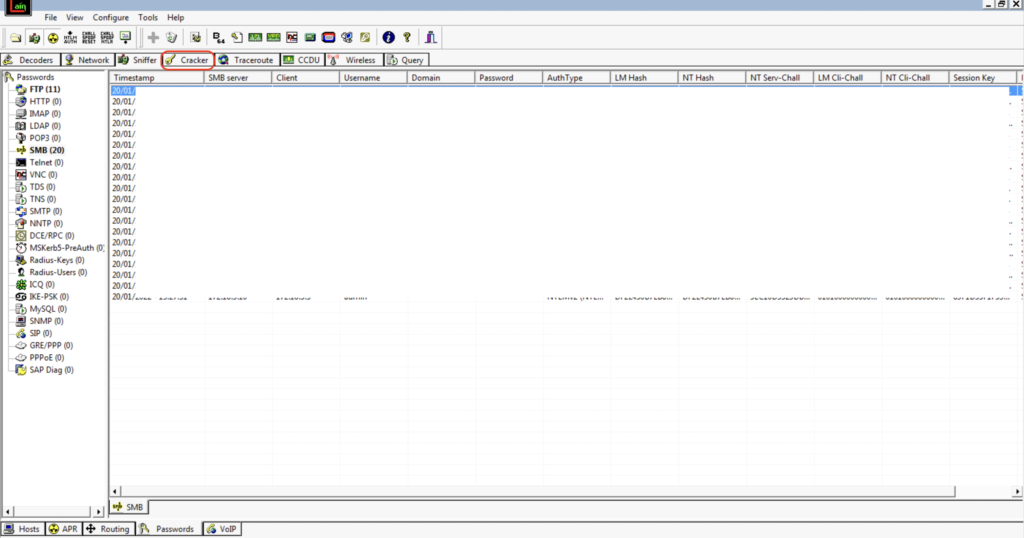
We will find the hash within the NTLMv2 Hashes section.

Right-click on the row and select Dictionary Attack
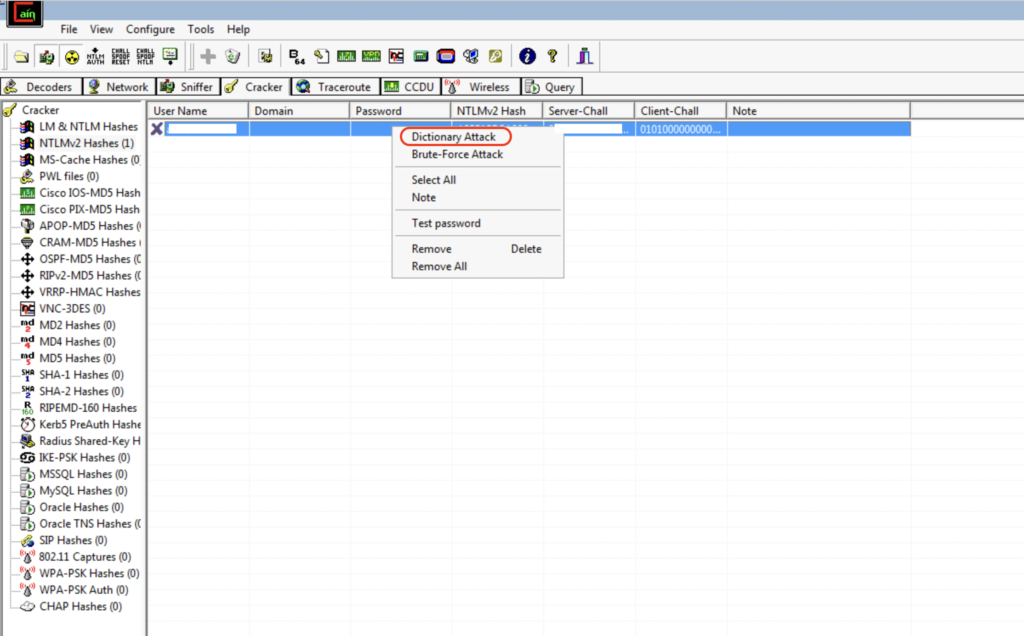
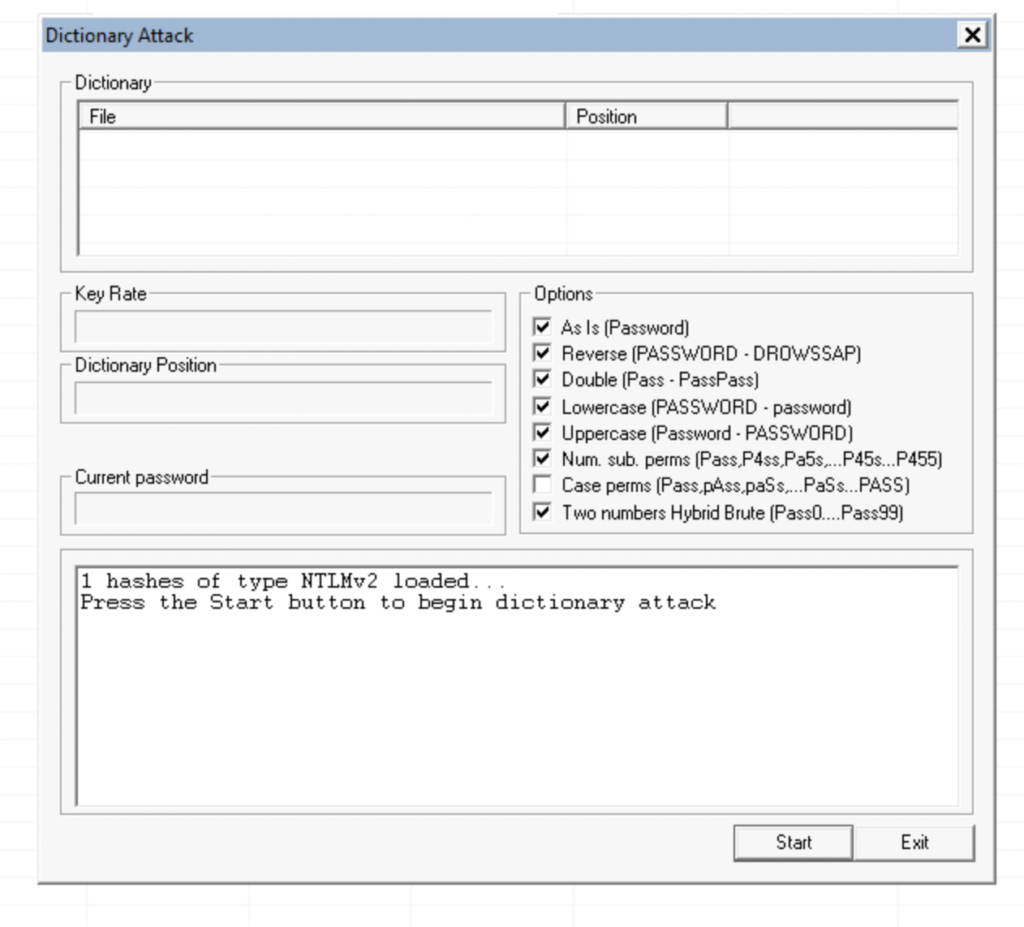
Right-click on the dictionary table and select Add to list
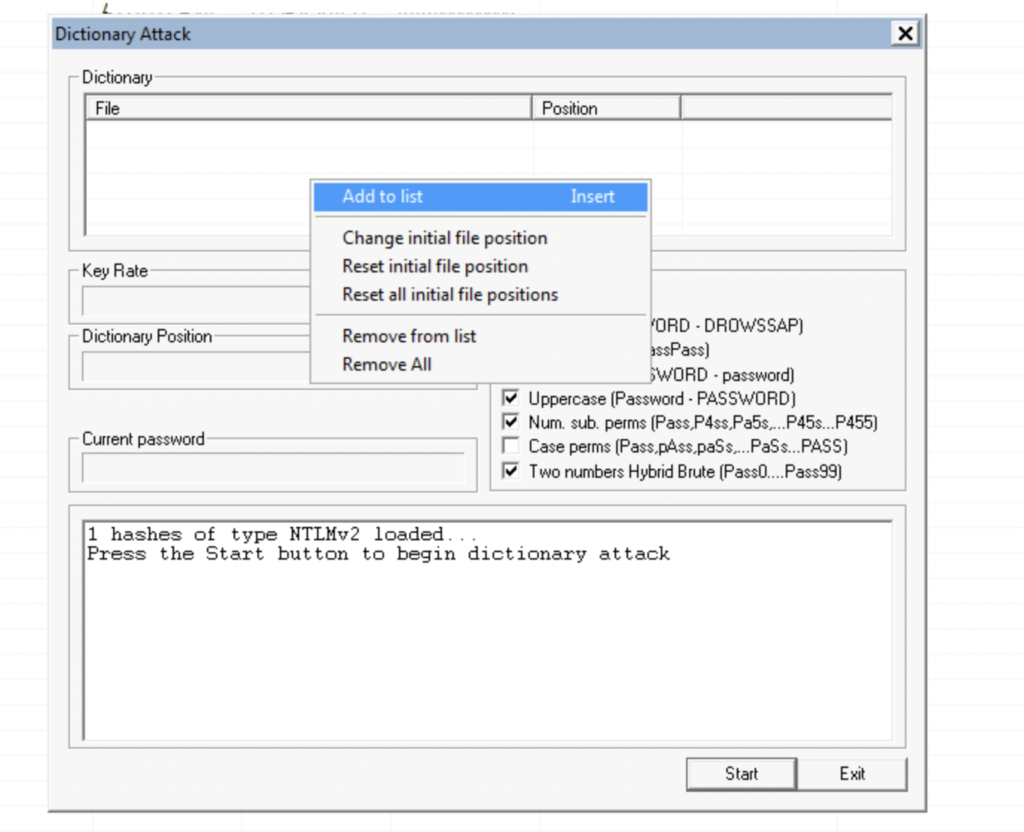
Add the wordlist available on the Desktop.


Initiate the dictionary attack, and after a couple of seconds, we should see the cracked password: xxxx.

Access the server
Access the server 172.x.x.10 using cain and abel.
Navigate to the Network tab.
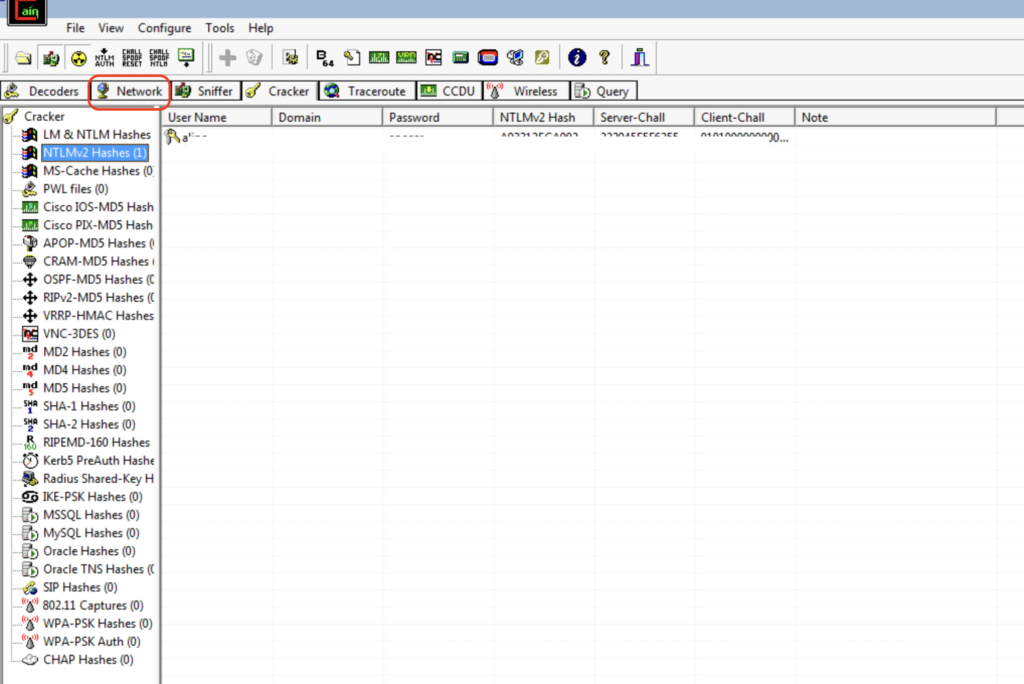

Right-click on the Quick List and select Add to Quick List.

Enter the host as 172.x.x.10
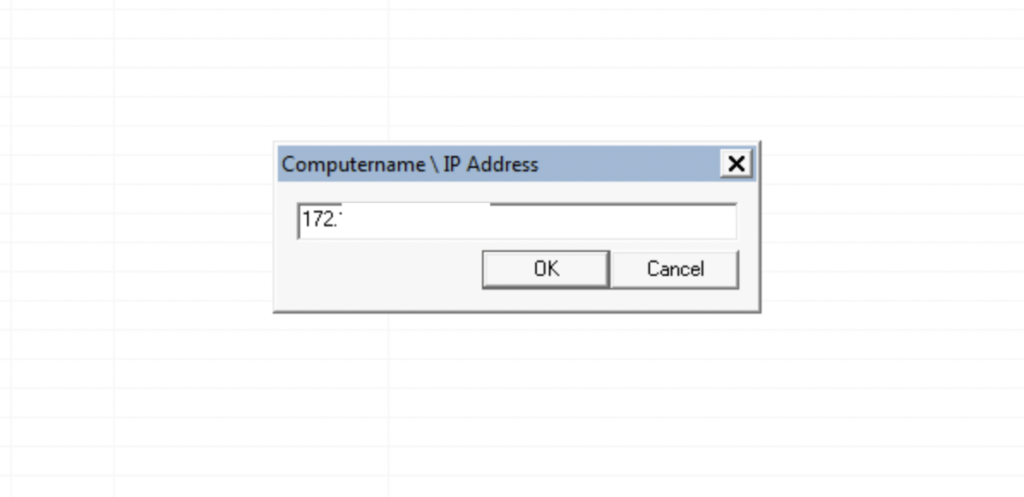
Once the host is added, right-click on the host and click “Connect As”.
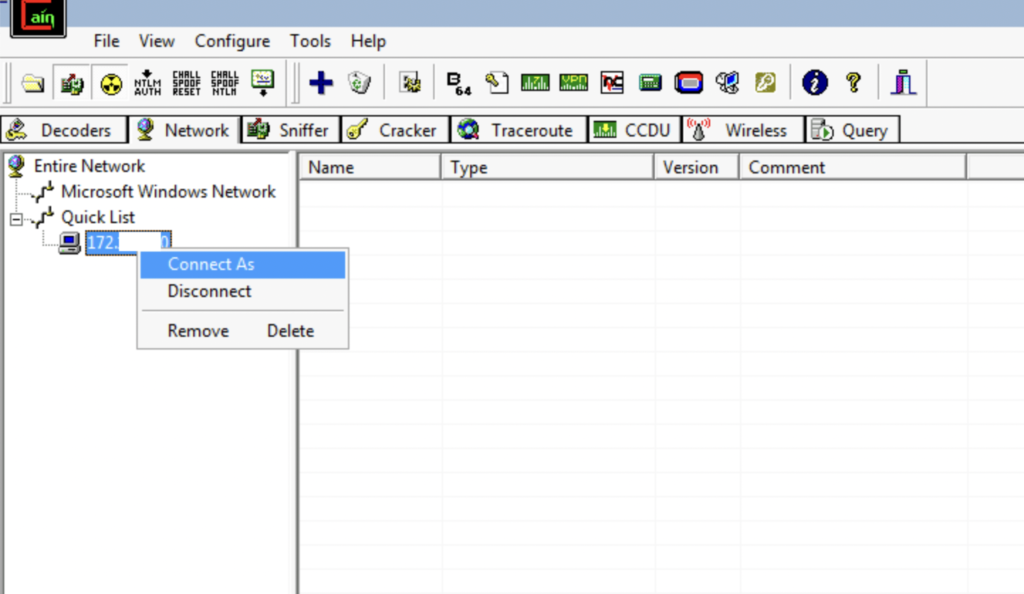
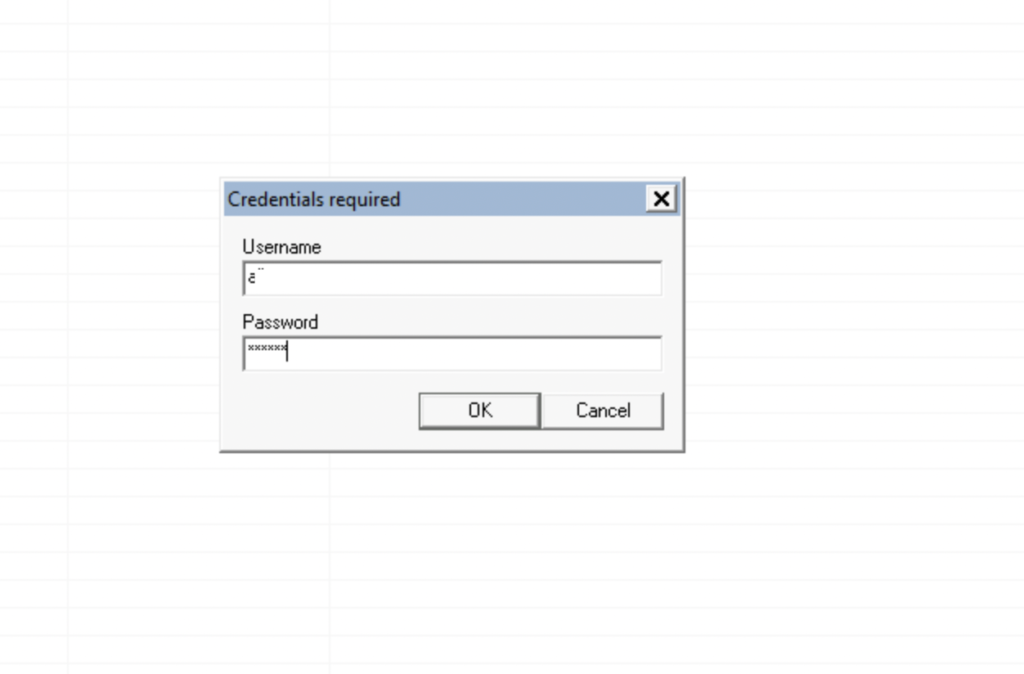
Then, provide the credentials cracked in Task 4: username:pass
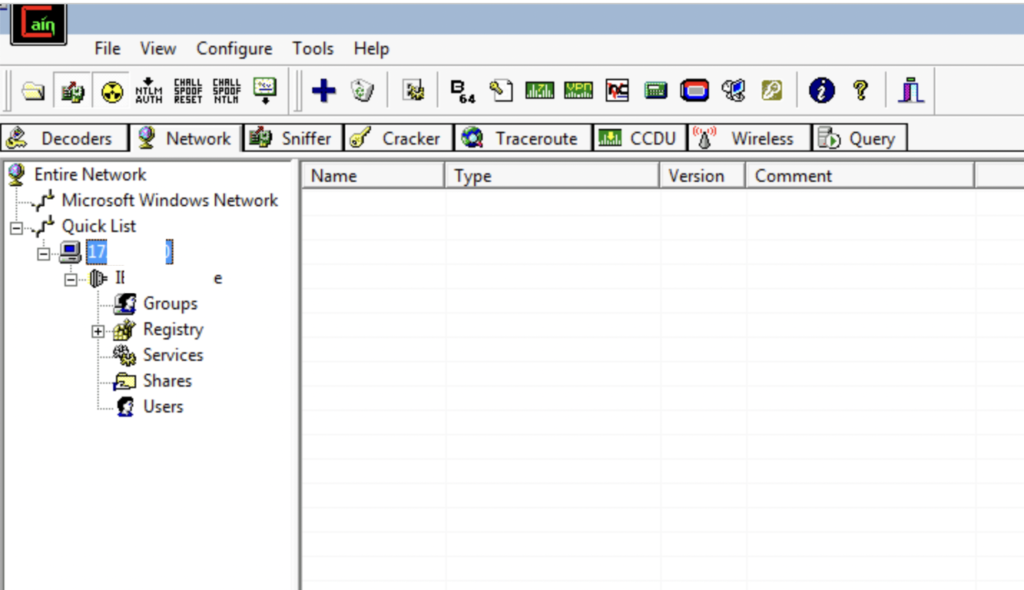
Click on the Services option.
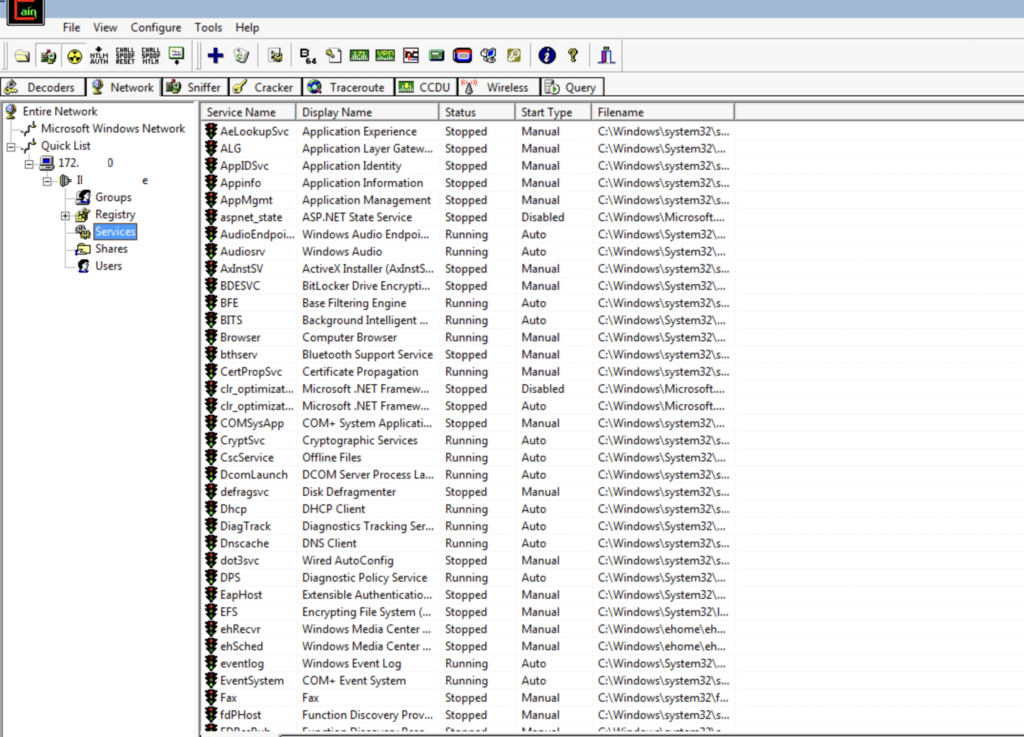
Right-click the Services options and select Install Abel:

Abel will appear in installed and running services.

Double click the computer icon (172.x.x.10) in order to refresh the view, and Abel should appear.
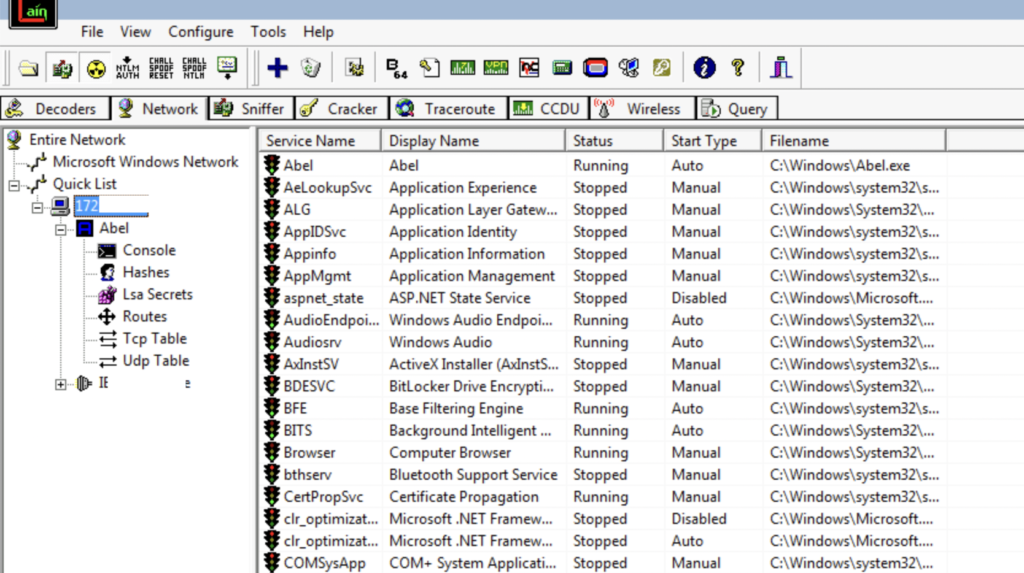
Let’s select the Console option. Here we have a shell on our target machine:
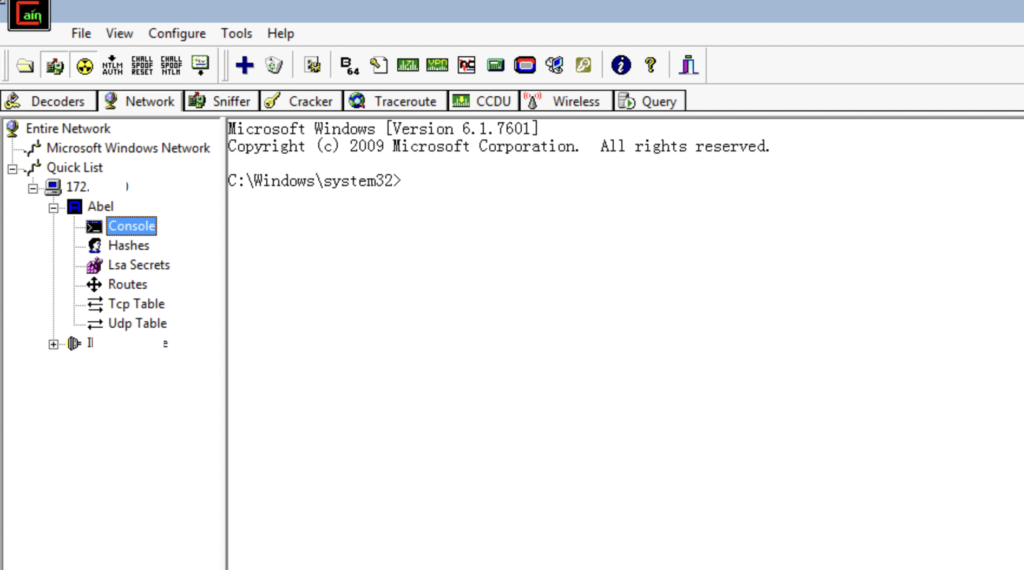
Execute commands on the server.
Commands:
whoami
hostname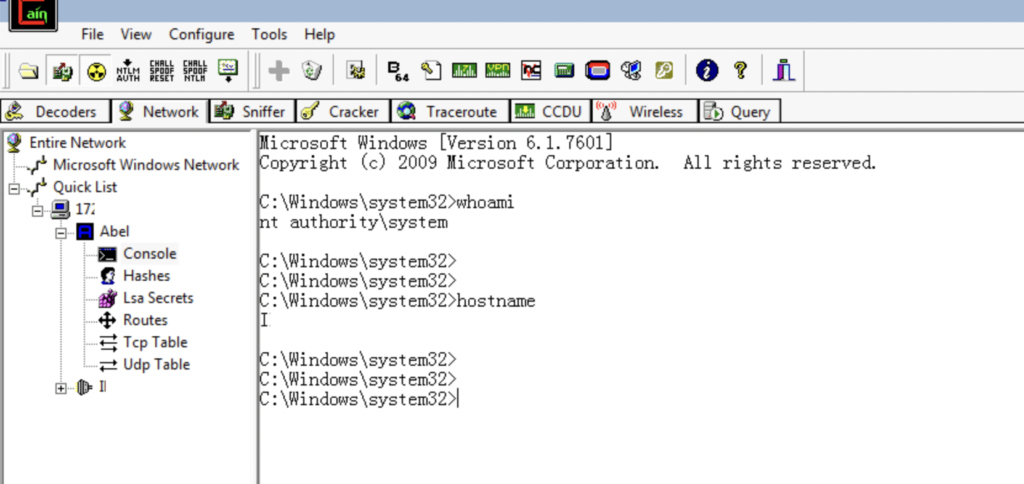


Leave a Reply